12
Neural Networks
Multi-layer Perceptron & Backpropagation
Theory
A Multi-layer Perceptron (MLP) is a feedforward neural network with one or more hidden layers. Backpropagation is the algorithm used to efficiently compute gradients for training. The algorithm uses the chain rule to propagate errors backward through the network.
Visualization
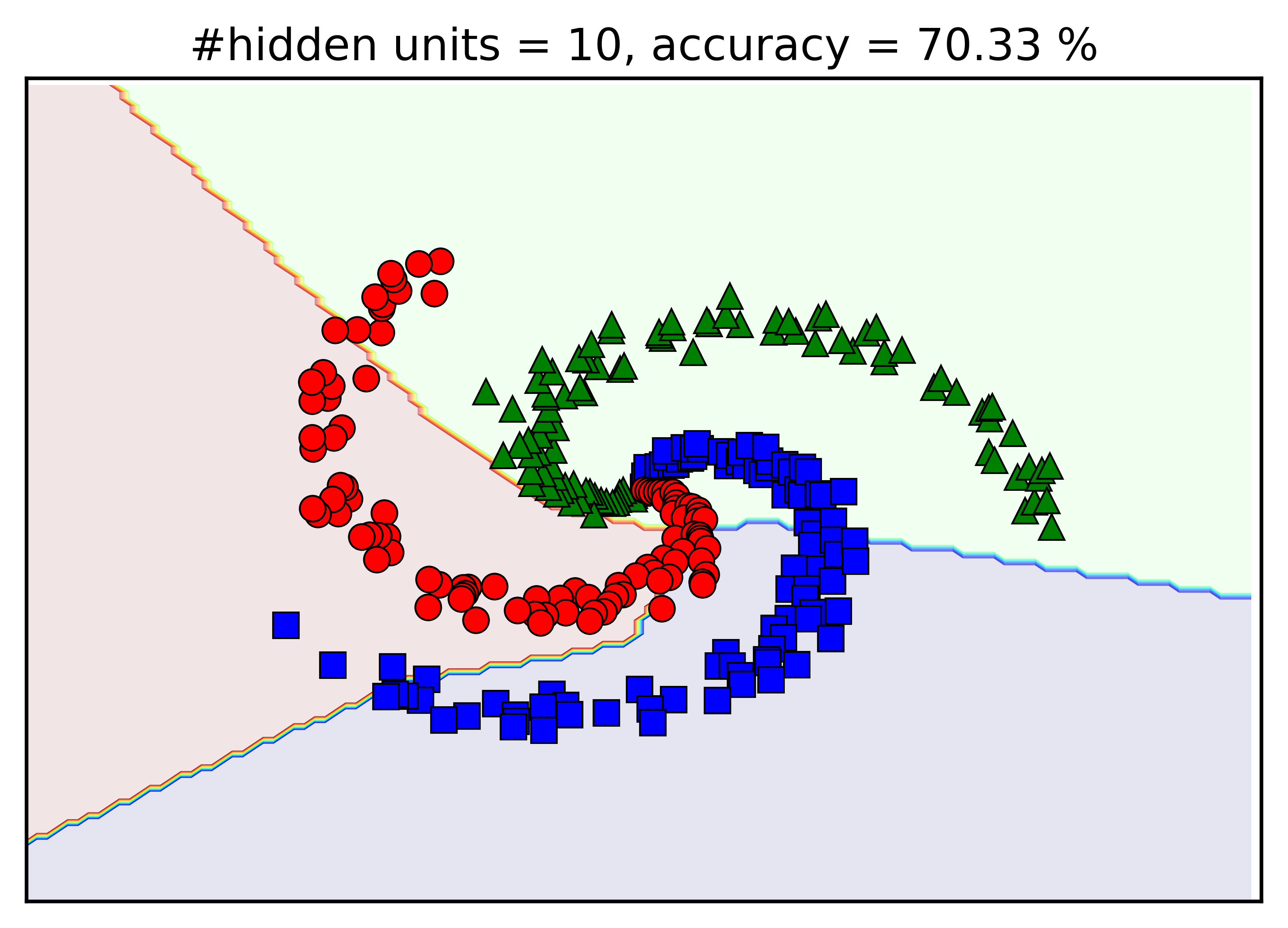
Mathematical Formulation
Forward Pass: z = Wx + b a = activation(z) Backpropagation (Chain Rule): ∂L/∂W = ∂L/∂a · ∂a/∂z · ∂z/∂W Common Activations: • ReLU: max(0, x) • Sigmoid: 1/(1+e⁻ˣ) • Tanh: (eˣ-e⁻ˣ)/(eˣ+e⁻ˣ)
Code Example
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Generate data
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=20,
n_informative=15, random_state=42)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.2
)
# Create MLP with 2 hidden layers
mlp = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(100, 50),
activation='relu',
max_iter=500,
random_state=42)
# Train
mlp.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Evaluate
train_score = mlp.score(X_train, y_train)
test_score = mlp.score(X_test, y_test)
print(f"Training Accuracy: {train_score:.3f}")
print(f"Test Accuracy: {test_score:.3f}")
print(f"Number of layers: {mlp.n_layers_}")
print(f"Number of iterations: {mlp.n_iter_}")