18
SVM
Soft Margin SVM
Theory
Soft Margin SVM allows some misclassifications to handle non-linearly separable data and improve generalization. The C parameter controls the trade-off between margin size and classification errors.
Visualization
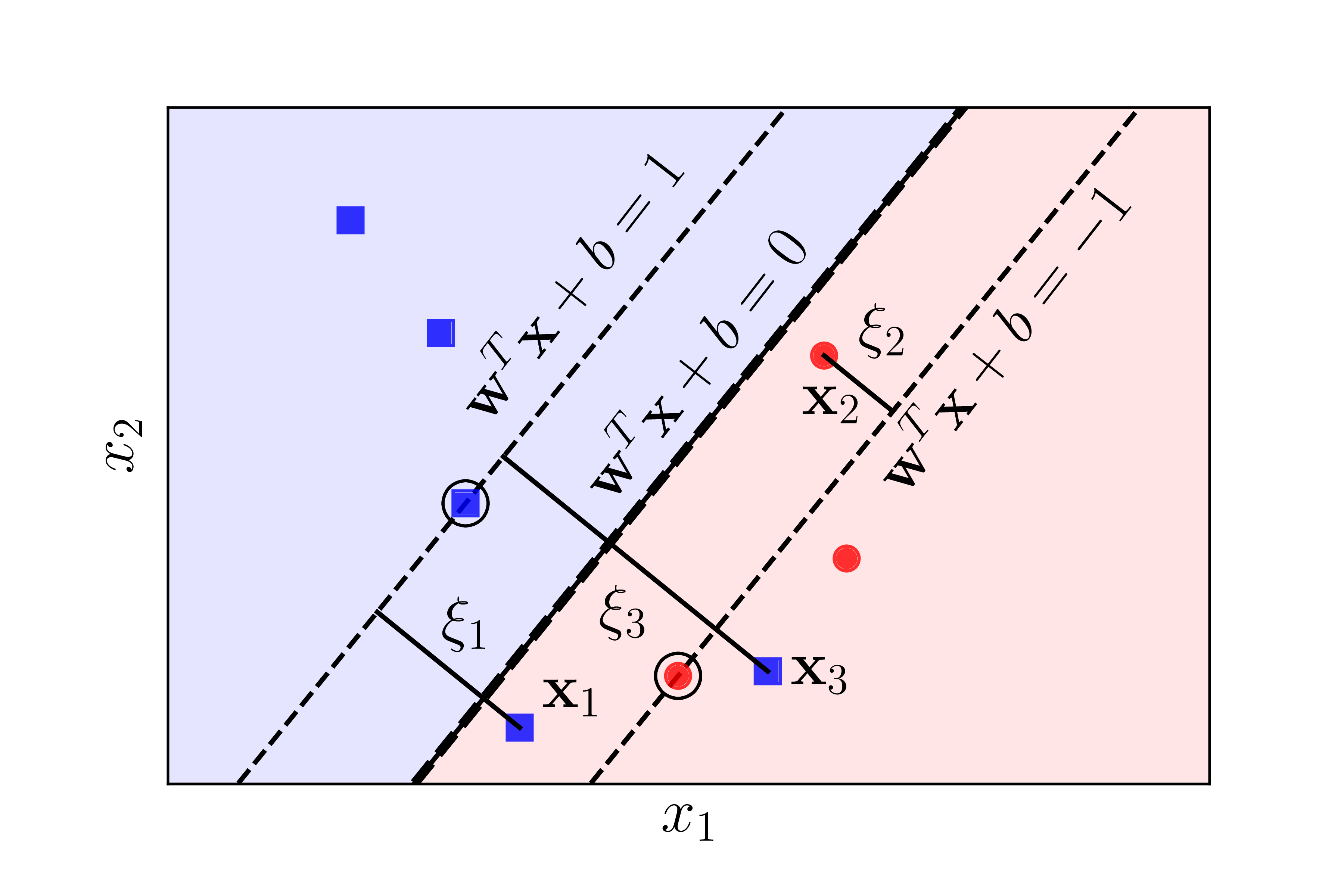
Mathematical Formulation
Formulation: minimize ½||w||² + C·Σξᵢ subject to yᵢ(w·xᵢ + b) ≥ 1 - ξᵢ, ξᵢ ≥ 0 C Parameter: • Large C: Hard margin (fewer violations) • Small C: Soft margin (more violations) Hinge Loss: max(0, 1 - yᵢ(w·xᵢ + b))
Code Example
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
import numpy as np
# Generate non-linearly separable data
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=200, n_features=2,
n_redundant=0, flip_y=0.1,
random_state=42)
y = np.where(y == 0, -1, 1)
# Train SVMs with different C values
C_values = [0.1, 1, 10, 100]
for C in C_values:
clf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear', C=C)
clf.fit(X, y)
accuracy = clf.score(X, y)
n_sv = len(clf.support_vectors_)
print(f"C={C:5.1f}: Accuracy={accuracy:.3f}, "
f"Support Vectors={n_sv}")
# Demonstrate trade-off
print("\nSmall C: More violations, simpler model")
print("Large C: Fewer violations, complex model")